The Plastic Predicament: Navigating Environmental Challenges in a Disposable World
The Impact of Plastic on Our Environment
Plastic, a versatile and widely used material, has become an integral part of our daily lives. From packaging to household items, plastic is ubiquitous in modern society. However, the convenience of plastic comes at a significant cost to our environment.
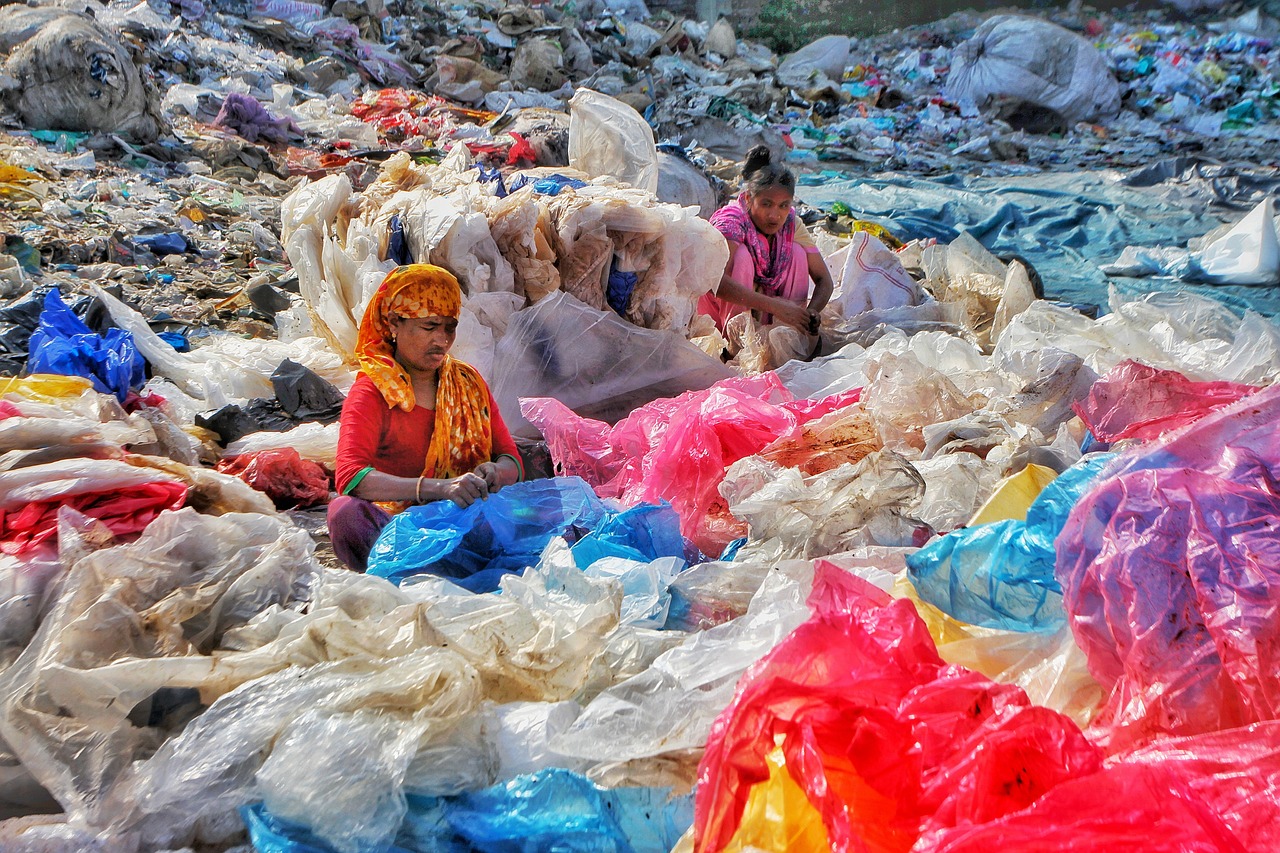
One of the most pressing issues related to plastic is its impact on marine life. Millions of tons of plastic waste end up in our oceans each year, posing a severe threat to marine animals. Sea turtles, seabirds, and marine mammals often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement that can be fatal.
Furthermore, the production and disposal of plastic contribute to environmental pollution and climate change. The extraction of fossil fuels needed to produce plastic releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming. Additionally, plastic waste that is not properly managed can leach harmful chemicals into soil and water sources, contaminating ecosystems.
To address the environmental challenges posed by plastic, it is crucial for individuals and industries to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing single-use plastics, recycling materials whenever possible, and promoting eco-friendly alternatives. Governments and policymakers play a vital role in implementing regulations that limit the use of non-biodegradable plastics and promote circular economy initiatives.
While the impact of plastic on our environment is significant, collective action and awareness can help mitigate its detrimental effects. By making conscious choices in our consumption habits and supporting initiatives that promote a greener future, we can work towards a cleaner and healthier planet for generations to come.
Understanding Plastic: Key Questions Answered
- Why is plastic banned?
- What is what is plastic made out of?
- What is plastic made of?
- What chemicals are in plastic?
- What does plastic mean in slang?
- What is the definition of plastic?
- When was plastic invented?
Why is plastic banned?
Plastic is often banned due to its detrimental impact on the environment. Single-use plastics, in particular, contribute significantly to pollution and pose serious threats to wildlife and ecosystems. These non-biodegradable materials take hundreds of years to decompose, leading to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans. The toxic chemicals released during the production and disposal of plastic further exacerbate environmental degradation and climate change. Banning plastic aims to reduce this environmental harm, promote sustainable alternatives, and encourage responsible consumption practices that prioritize the health of our planet for future generations.
What is what is plastic made out of?
Plastic is a synthetic material composed of polymers, which are long chains of molecules derived from various organic and inorganic compounds. The primary raw materials used in the production of plastic include petrochemicals such as ethylene and propylene, which are obtained from fossil fuels like crude oil and natural gas. These raw materials undergo a process known as polymerization, where they are chemically bonded together to form the polymer chains that give plastic its unique properties. Additionally, additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and colorants are incorporated into the plastic formulation to enhance its performance and appearance. The versatility and durability of plastic make it a widely used material in numerous industries, despite its environmental impact.
What is plastic made of?
Plastic is a synthetic material primarily composed of polymers, which are long chains of molecules derived from petrochemicals such as crude oil and natural gas. These polymers undergo a process called polymerization, where smaller molecules, known as monomers, link together to form the larger polymer chains that give plastic its unique properties. In addition to polymers, plastic may also contain additives like plasticizers, colorants, and reinforcements to enhance its strength, flexibility, and appearance. The specific composition of plastic can vary depending on the type of plastic being produced and its intended use.
What chemicals are in plastic?
Plastic is composed of a variety of chemicals, with the specific composition depending on the type of plastic being used. Common chemicals found in plastics include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These chemicals are added during the manufacturing process to provide different properties such as flexibility, durability, and transparency. However, some plastics may also contain additives like plasticizers, flame retardants, and colorants, which can pose potential health risks if they leach out of the plastic and into the environment or food products. It is important to be aware of the chemicals present in plastics and to use them responsibly to minimize any adverse effects on human health and the environment.
What does plastic mean in slang?
In slang terminology, “plastic” is often used to describe something or someone as fake, insincere, or superficial. When referring to a person as “plastic,” it implies that they are not genuine or authentic in their behavior or appearance. This slang term highlights the idea of being artificial or lacking true substance, akin to the characteristics of plastic material itself.
What is the definition of plastic?
Plastic is a synthetic material made from polymers that can be molded into various shapes and forms. It is a versatile substance known for its durability, flexibility, and lightweight properties. Plastics are commonly used in manufacturing a wide range of products, including packaging, containers, toys, furniture, and electronics. The term “plastic” encompasses a broad category of materials that can be classified based on their composition and properties, with different types of plastics serving specific purposes in different industries. Overall, plastic plays a significant role in modern society but also raises environmental concerns due to its longevity and impact on ecosystems if not properly managed.
When was plastic invented?
Plastic was invented in the late 19th century, with the first synthetic plastic known as Bakelite being developed by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in 1907. This marked a significant milestone in material science, as it introduced a durable and moldable substance that could be mass-produced for various applications. Since then, the evolution of plastics has revolutionized industries and everyday life, shaping modern society’s reliance on this versatile material for a wide range of products and purposes.